Master Good Software Engineering Practices for Reliable Builds
Learn essential good software engineering practices to improve code quality, boost productivity, and develop scalable, reliable software. Start now!

Good software engineering isn't about following a rigid set of rules. It’s about cultivating the proven habits and processes that help teams build software that actually works—reliably, at scale, and without causing headaches down the line. It's what separates simple coding from a true engineering discipline.
This approach is what keeps projects from collapsing under their own complexity and sets them up for success long after launch.
The Blueprint for Building Better Software
Think about what it takes to build a skyscraper. You wouldn't just start laying bricks and hope for the best. You'd need a detailed blueprint, constant safety checks, and a skilled crew that knows how to work together. Building software without a similar structure leads to the same kind of chaos: costly mistakes, endless rework, and an unstable final product.
That's where solid engineering practices come in—they are the blueprint for our digital world.
These practices are a collection of proven habits, collaborative workflows, and automated checks that guide a project from a rough idea to a polished application. Without them, teams quickly rack up technical debt. This isn't a financial term; it’s the price you pay later for taking shortcuts today. Over time, this debt piles up, making the system fragile, slow, and nearly impossible to update.
Core Pillars of Engineering Excellence
Adopting these practices isn't about adding red tape. It's about building a culture of quality and efficiency from the ground up. The goal is simple: catch problems early, make teamwork smooth, and create something that lasts.
This philosophy rests on a few key pillars:
- Predictable Quality: Automated tests and peer reviews ensure every line of code meets a high standard before it ever gets merged. No more "it worked on my machine."
- Enhanced Collaboration: When everyone uses the same tools and follows the same standards, developers can easily jump in, understand, and build on each other's work.
- Sustainable Scalability: Well-engineered software is built for growth. It can handle more users, data, and features without needing a complete overhaul.
- Increased Efficiency: Smart workflows and automation cut down on time wasted hunting for bugs, freeing up developers to focus on building things that matter.
Ultimately, good software engineering is about creating a system where doing the right thing is the easy thing. It's a proactive mindset that values long-term stability over short-term gains, ensuring the digital 'skyscraper' you build today stands tall for years to come.
Build a Foundation with Code Quality and Collaboration

Before a single feature gets built, the best engineering teams lay a strong foundation of quality and collaboration. These aren't just extra steps that slow you down; they're the very habits that prevent chaos down the road and actually speed things up in the long run.
Think of these principles as the bedrock for everything else you build. They set the ground rules for how your team interacts with the code—and each other—creating an environment where high-quality work is the natural outcome.
Use Version Control as a Collaborative Time Machine
At the core of almost all modern software development is version control, and Git is the undisputed king. Don't just think of it as a tool; it's a collaborative time machine for your entire project. It carefully tracks every single change made by every developer, giving you a complete, transparent history from the very first line of code.
This history is more than just a logbook—it's your safety net. If a new feature accidentally breaks something important, you can instantly "travel back in time" to a stable version without a full-blown crisis. More importantly, it gives developers a safe space to experiment. Anyone can create an isolated "branch" to work on a new idea without any risk to the main application. Once the feature is working perfectly, it can be merged back in.
Version control transforms development from a high-wire act into a structured process. It empowers teams to be bold and innovative, knowing they have a reliable system to manage complexity and reverse mistakes.
Reframe Code Reviews as a Learning Ritual
A code review is simply when developers check each other’s code before it gets added to the main project. Too often, teams treat this like a chore focused only on finding mistakes. But the real power comes when you reframe it as a knowledge-sharing ritual—a kind of peer coaching that makes both the code and the developers better.
During a good review, team members can:
- Share Knowledge: A senior developer might point out a more efficient way to solve a problem, while a junior dev could offer a fresh perspective that simplifies things.
- Ensure Consistency: Reviews are the perfect time to make sure everyone is following the team's agreed-upon style, keeping the codebase clean and uniform.
- Catch Logic Flaws: A second pair of eyes is amazing at spotting subtle bugs or logical errors the original author might have overlooked.
This process doesn't just improve the code being reviewed; it helps level up the entire team’s skills over time.
Establish Coding Standards as a Shared Language
If version control is the project's history book, then coding standards are its shared grammar. These are simply a set of guidelines that define the team's style for writing code. They cover everything from how you name variables to how you structure files.
This might sound like a small detail, but the impact is massive. When everyone writes code that looks and feels the same, it becomes instantly easier for anyone on the team to read and understand. This dramatically reduces the mental effort needed to work on an unfamiliar part of the codebase, which makes maintenance and debugging way more efficient. Over time, this discipline is one of the best ways to fight off technical debt. If your team is ready to get serious about this, mapping out a formal process for a code cleanup is a great next step.
How strictly teams adopt these practices often depends on their size, but the positive impact is consistent. A 2020 empirical study found that larger teams are more likely to formally adopt practices like version control, code reviews, and automated testing. The result? They see fewer defects, build more reliable products, and find it easier to collaborate as they grow. Together, these foundational habits create a culture where quality isn't just an afterthought—it's woven into the entire development process.
Streamline Your Workflow with Agile Methodologies

While great code and teamwork are the bedrock of any project, the process you follow is what truly sets the pace. This is where Agile methodologies come in, shifting teams away from rigid, long-term roadmaps and toward a more flexible, responsive way of working.
Think of it like planning a road trip. The old-school approach, known as the Waterfall model, is like mapping out every single turn, gas station, and motel before you even leave your driveway. That sounds great in theory, but the plan shatters the second you run into a surprise detour or a traffic jam.
Agile is different. It’s like planning your trip one leg at a time. You pick a destination for the day, you drive, and then you adjust tomorrow's plan based on what happened today. This iterative rhythm is one of the most powerful good software engineering practices because it helps teams adapt to the unexpected and deliver real value, fast.
Breaking Down Agile Into Actionable Concepts
At its heart, Agile is all about slicing massive projects into small, digestible chunks. Two of the most common ways to do this are with frameworks like Scrum and Kanban. They might look a bit different, but they share the same goal: keep work and feedback flowing continuously.
Scrum, for example, structures work into sprints. These are short, fixed periods—usually one to four weeks—where the team commits to finishing a specific list of tasks. It's like a mini-project with a very clear finish line. This intense focus keeps the team from getting bogged down and ensures they’re constantly shipping functional pieces of the software.
To make those sprints work, tasks are often captured as user stories. These aren't technical specs; they're simple, human-centric descriptions of a feature from the user's point of view.
Most user stories follow a simple template:
- As a [type of user]…
- I want to [do something]…
- So that I can [achieve a goal].
This little formula is surprisingly powerful. It constantly reminds everyone why they’re building something and who they're building it for.
The Team GPS: Tools like Jira and Trello
To keep all these moving parts from descending into chaos, Agile teams lean on project management tools like Jira or Trello. Think of these tools as a shared GPS for the entire team. They offer a crystal-clear, visual map of the project, showing what’s in progress, what’s up next, and where things might be getting stuck.
Agile is not just a buzzword; it’s a practical system for building better products by embracing continuous feedback. It shifts the focus from rigid, upfront planning to adaptive execution, allowing teams to respond to customer needs and market changes with speed and precision.
Adopting these frameworks is a big cultural shift, no doubt about it. For any team thinking about making the jump, knowing the practical steps is key. You can dive deeper into the nitty-gritty in our guide on https://www.42coffeecups.com/blog/agile-methodology-implementation. When it clicks, you'll find your team delivering a better product, faster than you thought possible.
To take this efficiency even further, many teams are weaving automation into their development cycles. Using app development automation services can supercharge an Agile workflow by handling repetitive tasks, which frees up developers to focus on what matters. This blend of smart process and smart technology is what truly separates good teams from great ones.
Automate Quality with a Modern Testing Strategy
If you think building quality software means a frantic, last-minute bug hunt right before launch, think again. The best teams have moved on from that chaotic approach. Instead, they treat testing as a continuous safety net, woven directly into the development process from the very first line of code.
This isn't about adding another step; it's a fundamental shift in mindset. Testing becomes an automated, ever-present guardian of your code quality, not a final, manual gate. This is easily one of the most impactful good software engineering practices you can adopt. It turns quality control from a slow, error-prone task into a reliable system that gives you constant feedback.
Demystifying the Layers of Software Testing
So, how does this actually work in practice? Think of it like building a car. You wouldn't assemble the entire vehicle and only then check if the spark plugs work. That would be insane. You test each component at every single stage, and software is no different.
-
Unit Tests (Checking the Smallest Parts): These are your bread and butter. Unit tests focus on the smallest possible piece of code, like a single function, completely on its own. In our car analogy, this is like testing each spark plug, bolt, and wire individually to make sure it's flawless. They're fast, simple to write, and form the foundation of any solid testing strategy.
-
Integration Tests (Ensuring Parts Work Together): Once you know the individual components are good, you need to see if they play nicely together. Integration tests check the handoffs between different modules or services. This is like connecting the engine to the transmission and making sure they communicate correctly without grinding gears. These tests are crucial for catching the "interface" bugs that unit tests can't see.
-
End-to-End Tests (The Final Test Drive): This is the ultimate check. An end-to-end (E2E) test mimics a real user's journey through your entire application—from logging in, to adding an item to a cart, to successfully checking out. It’s the equivalent of taking the fully assembled car for a spin on a real road. It confirms the whole system works exactly as a user would expect.
This pyramid visualizes how these tests should be balanced. You want a wide base of fast, simple unit tests, with fewer, more complex tests as you move up.
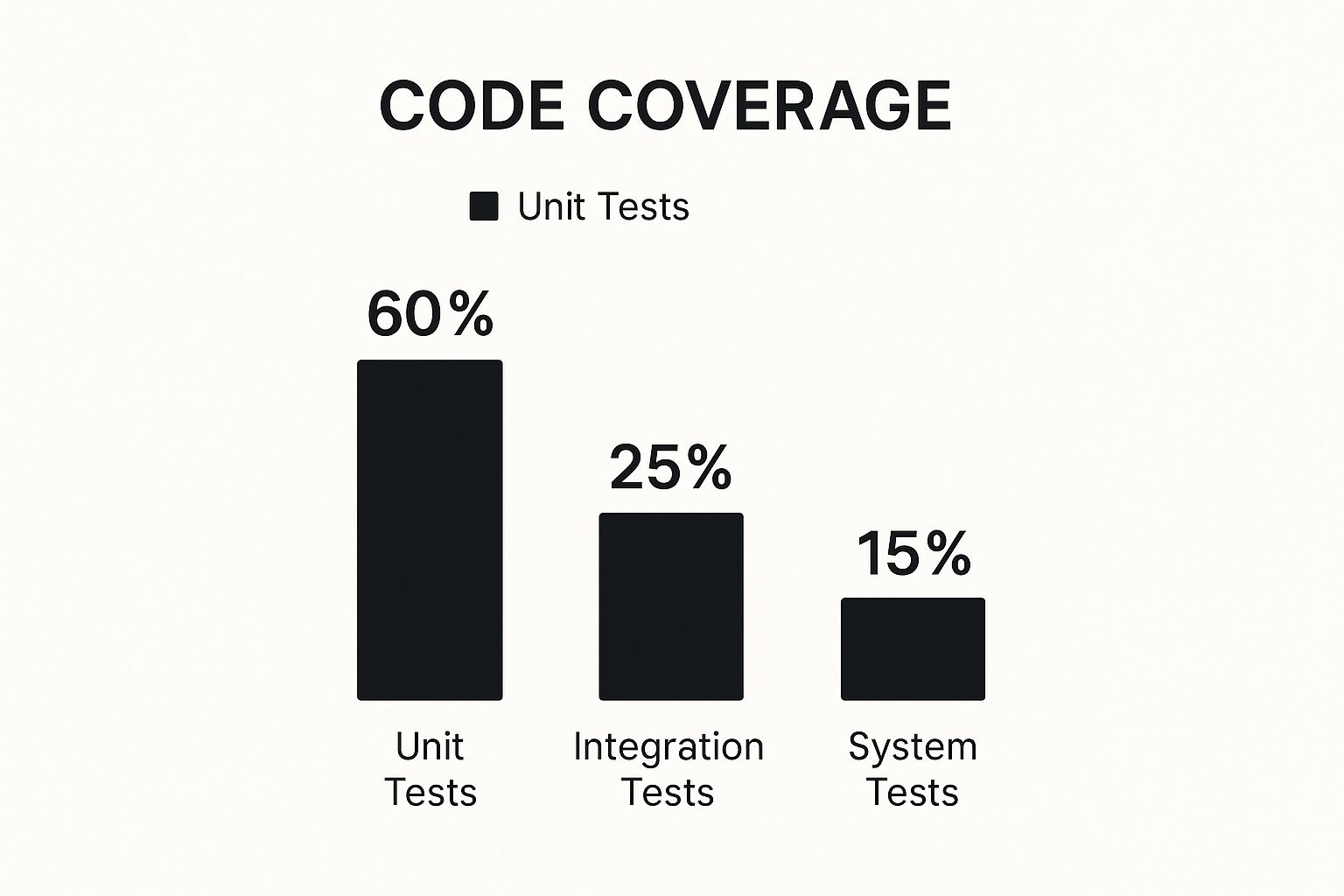
As you can see, the vast majority of your effort should go into unit tests. They give you the biggest bang for your buck by catching bugs early and quickly.
To give you a clearer picture, here's a simple breakdown of the main testing strategies.
A Comparison of Key Testing Strategies
This table outlines the primary types of software testing, what they aim to achieve, and where they fit best in the development cycle.
| Testing Type | Primary Goal | Scope | When to Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unit Testing | Verify that a single, isolated piece of code works as intended. | A single function or component. | Continuously, during development. Run with every code change. |
| Integration Testing | Ensure that different modules or services can communicate and work together correctly. | Interaction between 2+ modules. | After unit tests pass, before full system testing. |
| End-to-End (E2E) Testing | Validate the entire application flow from a user's perspective. | The full application stack. | Before a release, to simulate real-world usage. |
| Performance Testing | Check how the system behaves under a specific workload (speed, scalability, stability). | The entire system under stress. | Before launch and after major changes. |
Understanding these distinctions is key to building a comprehensive quality net that catches issues at every level, not just at the finish line.
Building an Automated Factory Assembly Line for Code
Just having different types of tests isn't enough. The magic happens when you automate them within a Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) pipeline.
Think of CI/CD as an automated factory assembly line for your code. Every single time a developer pushes a change, this assembly line kicks into action.
-
Continuous Integration (CI): The moment new code is checked in, the system automatically builds the application. It then runs all the unit and integration tests to instantly verify that the new change hasn't broken anything. If a test fails, the developer gets an immediate alert. They can fix the bug right away, while the code is still fresh in their mind. This simple feedback loop prevents the dreaded "integration hell," where days of work are lost trying to untangle conflicting changes.
-
Continuous Delivery (CD): Once all the automated tests pass, the CD part of the pipeline takes over. It automatically packages the new version of the software and gets it ready for release. From there, it might be deployed to a staging environment for a final look, or if you're really confident, pushed directly to your users.
This automated pipeline is the engine of modern software development. It transforms releases from a risky, stressful event into a routine, low-risk activity. Teams with strong CI/CD practices can confidently release updates multiple times a day, not just a few times a year.
By automating this whole process, teams catch errors in minutes instead of weeks, which dramatically reduces the cost and effort of fixing them. This deep commitment to quality ensures your software stays stable, reliable, and easy to improve over its entire life.
To go even deeper, check out these excellent insights into building robust software quality assurance processes.
2. Embrace Cloud Infrastructure and Modern Tooling

Great code and slick workflows are one thing, but they need a solid foundation to run on. Not too long ago, "going live" meant buying, racking, and maintaining physical servers in a closet or data center. It was a slow, expensive, and frustratingly rigid process.
Today, top-tier engineering teams build on the cloud, and it has completely changed the game.
Think of it like this: you could spend years and a small fortune building your own factory from the ground up. Or, you could just rent space in a cutting-edge industrial park that offers unlimited power, specialized equipment, and a global logistics network on day one. It’s a no-brainer, and that’s exactly what platforms like Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure provide for software.
These platforms give teams instant, on-demand access to massive computing power, managed databases, and powerful services for things like machine learning. This direct link between cloud adoption and business speed is one of the most critical software engineering practices today.
How the Cloud Unlocks Faster Development
Using the cloud isn't just about renting someone else's computers; it fundamentally speeds up the entire development lifecycle. Instead of filing a ticket and waiting weeks for a new server, a developer can spin up an entire environment with a few clicks, test out a new idea, and then tear it all down when they're finished.
This agility delivers some huge advantages:
- Global Reach: Easily deploy your application in data centers all over the world. This gets your software closer to your users, making it faster and more reliable for everyone.
- Automatic Scalability: Set up your app to handle sudden spikes in traffic automatically. If a marketing campaign goes viral, the cloud can instantly add more resources to keep your site from crashing, all without a person lifting a finger.
- Serious Uptime: Cloud providers have built-in redundancy and failover systems. This makes your application far more resilient to hardware failures than anything you could realistically build yourself.
- Fewer Operational Headaches: The provider handles the physical security, network upkeep, and hardware swaps. This frees up your team to focus on building features that matter, not managing servers.
Adopting cloud platforms allows teams to move faster, experiment more freely, and build more resilient applications. It offloads the undifferentiated heavy lifting of infrastructure management so engineers can focus on creating value.
The impact of this shift is undeniable. As of 2024, nearly 69% of businesses worldwide have moved to the cloud to accelerate their operations. In fact, companies that embrace cloud platforms have seen an incredible 53% faster revenue growth than their counterparts. You can dig into more data on software development trends to see the full picture.
Manage Your Infrastructure with Code Blueprints
To take the power of the cloud even further, modern teams practice Infrastructure as Code (IaC). This means that instead of manually clicking around in a web console to configure servers and databases, you define your entire setup in configuration files—just like application code.
Think of IaC as creating a master blueprint for your entire server environment. This blueprint lives in version control (like Git) right alongside your app's code, turning infrastructure from a manual, error-prone chore into a predictable and automated process.
Tools like Terraform or AWS CloudFormation read these blueprints and automatically build the exact environment you described. Need a perfect replica of your production environment for testing? You can have it in minutes. Need to recover from a disaster? Just redeploy from the blueprint.
By treating your infrastructure like code, you get all the benefits of versioning, collaboration, and automation, making your systems more reliable and consistent than ever.
Frequently Asked Questions
Knowing what good software engineering looks like is one thing. Actually putting it into practice in the real world? That’s where things get tricky. Let's tackle some of the common questions and hurdles teams run into when they try to adopt these principles.
How Can a Small Team or Solo Developer Implement These Practices?
This is a great question. For small teams and solo devs, the biggest mistake is trying to do too much at once. You don't need to copy Google's entire development infrastructure. The key is to start small and focus on what gives you the most bang for your buck.
- For Solo Developers: If you do nothing else, use Git. It’s your safety net, your time machine, and your project's single source of truth. It costs nothing to set up and will absolutely save your skin one day.
- For Small Teams: Build on that foundation. Start with Git, then add a simple code review process. You'd be amazed how many bugs and design flaws you can catch just by having one other person put their eyes on the code before it gets merged.
The point isn't to be perfect overnight. It’s about making small, smart improvements. Focus on consistency, safety, and quality at a scale that actually works for your team.
What Is the Most Important Practice to Start With?
If you can only pick one thing, make it version control—specifically, Git. It is the bedrock of modern software development. Without it, almost every other good practice falls apart.
Think about it: collaboration becomes a mess of conflicting files, rolling back a bad change is a manual nightmare, and automating anything is next to impossible. Version control is the one change that makes everything else easier and more effective, no matter the size of your project.
How Do You Get Team Buy-In for Adopting New Practices?
This is all about psychology, not authority. You can't just force new rules on people and expect them to stick. The secret is to show how a new practice solves a real, nagging problem your team is already facing.
Find the pain point. Are releases always stressful and buggy? Is the codebase a tangled mess that everyone's afraid to touch? Frame the new practice as the direct solution. For instance, you could introduce automated tests not as a chore, but as a way to stop spending weekends manually testing everything.
Start small. Run a pilot with a couple of team members who are open to the idea. Once you have a clear win—a smoother release, a nasty bug caught early—the rest of the team will see the benefits for themselves. Success is a much better motivator than a mandate.
Ready to build a high-performance web application grounded in the best engineering practices? 42 Coffee Cups specializes in helping businesses accelerate growth with scalable, reliable software. Discover how our expert development teams can help you deliver your next project.